WHY IS AN EXPLOSION RIST ASSESSMENT NECESSARY?
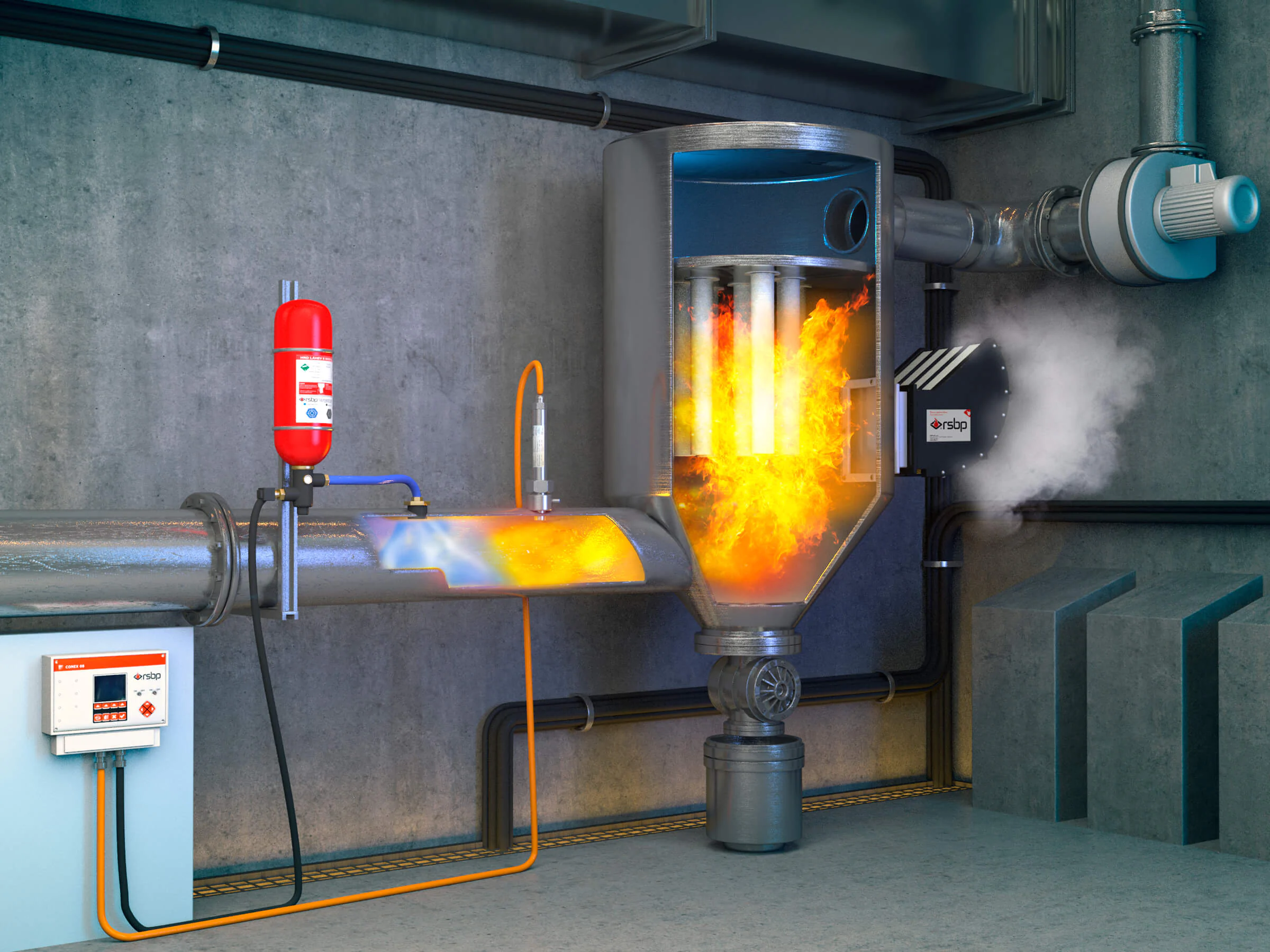
Dust is generated in industries handling loose products. When combined with oxygen in the air, it forms an air/dust mixture with explosive and flammable properties.
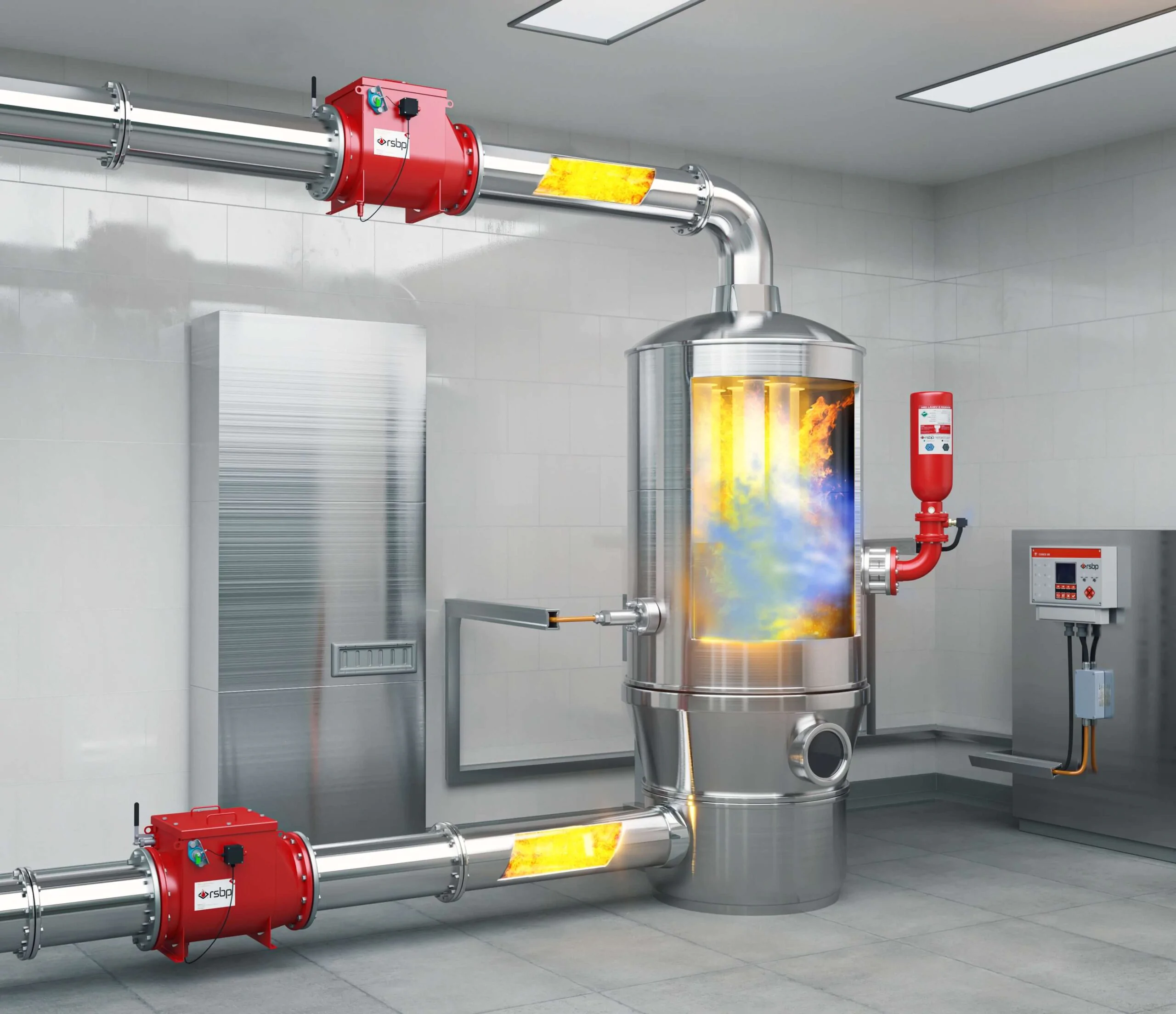
Overheated surfaces, a spark from static electricity and other sources of initiation cause it to ignite and explode locally. The shockwave displaces the burning aerosol suspension further, and the primary explosion is followed by a secondary explosion - much more powerful and destructive.
To prevent an explosion, hazardous contact must be avoided. Dust cannot be eliminated - it is an unavoidable by-product of operational and production processes. Similarly, it is impossible to eliminate oxygen because people need to breathe.
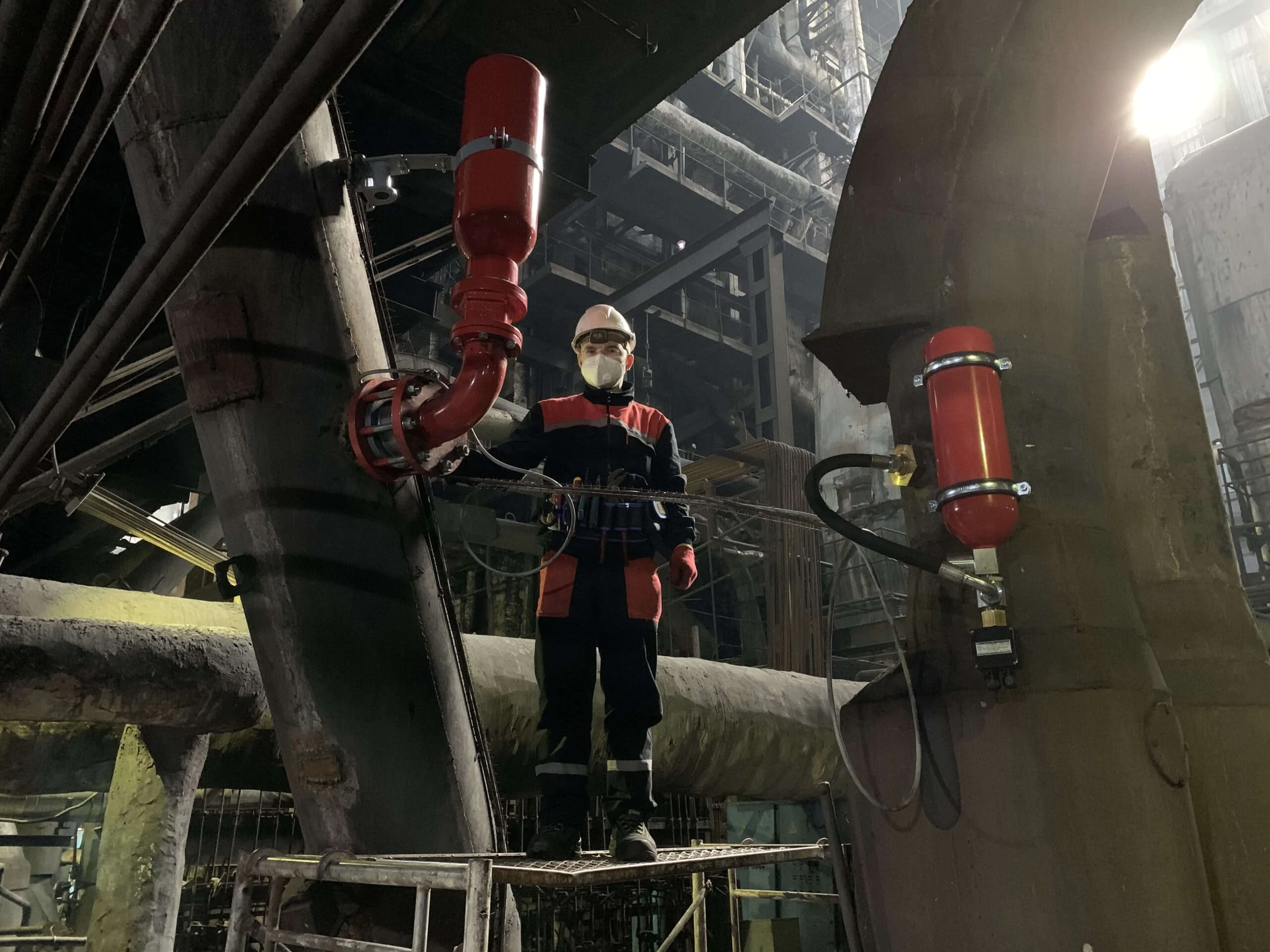
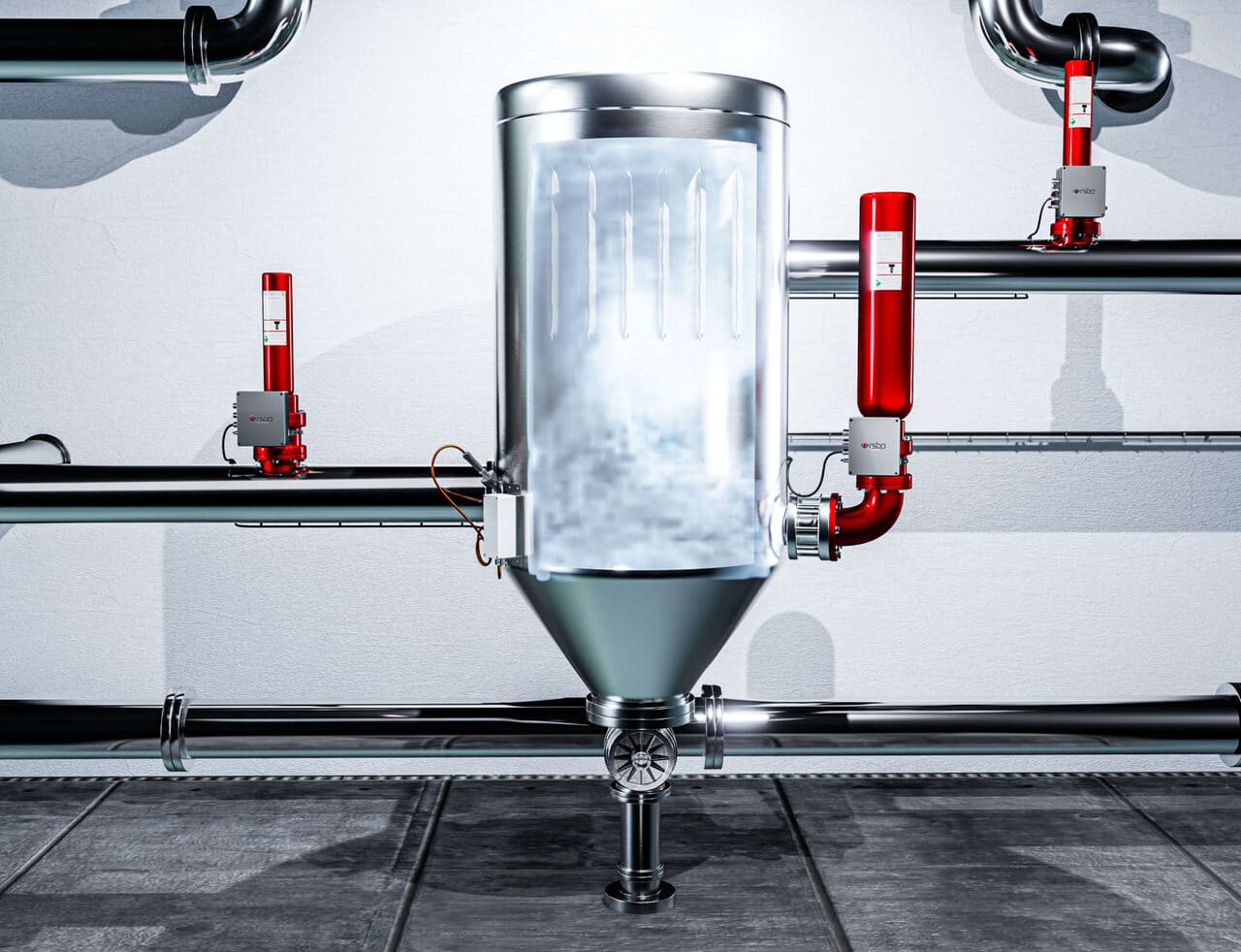
The solution is to identify sources of dust generation, dust accumulation, classify them as hazardous areas and exclude their contact with ignition sources as much as possible. Where this is not possible, apply explosion protection systems.
European ATEX directive 153 (directive 99/92/EC) requires owners of hazardous facilities to protect personnel from accidents, including explosions.
The operator company must:
- Carry out a risk assessment taking into account the probability of an explosive atmosphere;
- Classify and mark hazardous areas;
- Install explosion protection devices on the equipment.
ATEX audit (Explosion Risk Assessment) includes a risk assessment, explosion protection and the organisation of tests, if necessary. During the audit, experts verify compliance with requirements of IEC 60079-10-2:2015, ATEX 114 (2014/34/EU).
These standards set out the requirements for the classification of hazardous areas and the safety of equipment for use in potentially explosive environments.
The purpose of the explosion protection analysis is to identify the hazards associated with combustible dust and explosive dust atmospheres in production and to develop measures to protect equipment and personnel against dust explosions.
What are the purposes of an audit:
- Identify hazards based on the characteristics of the substances handled in the workplace;
- Determine their quantities and the probability of an explosive environment forming;
- Identify possible ignition sources;
- Identify the potential damaging factors of an explosion;
- Assess the risks;
- Develop mitigation measures.