Introduction
Combustible metal dust explosion hazards are a serious safety hazard for many heavy industry facilities. In this article we explore the reasons for the high explosion hazard of metal particles and discuss the protective measures needed to prevent tragedies.
What is metal dust?
Dust is airborne particulate matter suspended in the air, ranging in size from a few fractions to hundreds of microns.
Metal dust is very small particles of metals, usually between 1 and 1000 micrometers in size. They are generated during manufacturing processes and can consist of various metals and their alloys, depending on the source.

How is metal dust formed?
Metal particles are often generated when metal is machined with abrasive tools.
The formation of explosive metal particles accompanies the processes:
- Machining of metals. Grinding, turning, milling, cutting, drilling – these processes produce fine chips.
- Welding and surfacing. Evaporation of metal at high temperatures leads to the formation of condensate, which subsequently forms fine particles.
- Casting. Destruction of casting molds, machining of castings.
- Abrasive blasting. Sandblasting, polishing.
- Powder metallurgy. Metal dust is a source material for manufacturing products by powder metallurgy methods.
- Production and processing of ores. Crushing, grinding of ore.

The technological processes mentioned above involve equipment, the operation of which is highly likely to contain explosive metal dust:
- Metal grinding and polishing equipment
- Welding equipment
- Metal cutting equipment (including plasma cutting)
- Powder mixers
- Metal spraying machines
- 3D printers
- Aspiration and ventilation systems
- Bunkers and silos
- Crushers, mills, separators
Metal dust in this equipment can be found in steel mills, mechanical and aeronautical engineering, mining and manufacturing, and foundries.
Why can metal dust be flammable?
Dust ignition conditions
The following conditions are necessary for particles to burn and further explode:
- The presence of an ignition source (e.g., a spark from a short circuit)
- The presence of an oxidizing agent (oxygen) in the required concentration.
- Dust in suspension in a limited volume of air.
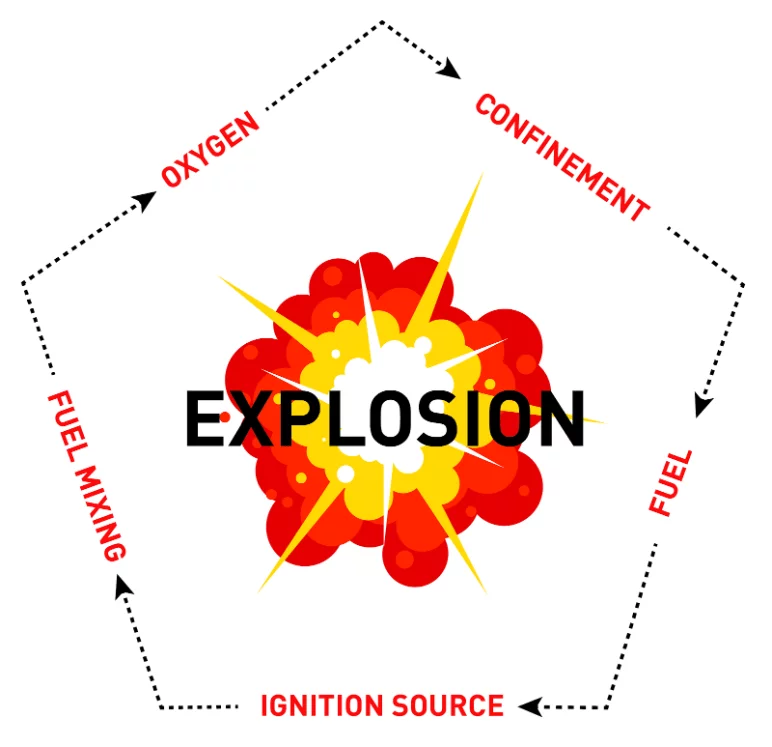
If these conditions are present, metal dust can ignite and cause an explosion inside the premises or industrial equipment.
Self-ignition mechanisms
Metal dusts can self-ignite because many metals can actively engage in an exothermic oxidation reaction with oxygen, which can cause the release of large amounts of heat. Self-ignition occurs when the oxidation reaction is accelerated to such an extent that the heat released doesn’t have time to dissipate, and the temperature reaches the ignition point.

The influence of particle size
The flammability of metal dusts is directly related to particle size. The greater their dispersion, the smaller their Lower Concentration Limit of Flame Propagation (LEL, g/m³). Dusts with an LEL below 65 g/m³ are classified as explosive substances, while substances with an INRR below 15 g/m³ belong to the first hazard class.
The LEL of aluminum powder is 40 g/m³. However, for fine aluminum powder (particle size 63 μm), the LEL can be as low as 15 g/m³.
Examples of flammable metal dusts
Each type of metal powder has individual quantitative explosion hazard characteristics – explosion hazard index (Kst) and maximum explosion pressure (Pmax). The higher the Kst, the more hazardous the dust.
It is important to realize that Kst and Pmax are experimentally determined parameters and their values may vary depending on the particle composition, concentration and dispersion. The exact value of Kst and Pmax at a particular object can be determined by ATEX.CENTER specialists during laboratory tests.
Dusts with Kst > 300 bar⋅m/s are usually classified as "extremely explosive".
Examples of different types of metal dusts with explosion hazard characteristics.
| Dust type | Kst, bar⋅m/s | Pmax, bar |
|---|---|---|
| Zinc | 20-50 | 5-8 |
| Iron | <100 | 5-7 |
| Titanium | 200-500 | 7-12 |
| Magnesium | 400-600 | 7-10 |
| Aluminium | 200-800 | 6-10 |
Based on the Kst values, we can conclude that the most explosive dust of the listed is aluminum dust. Nevertheless, all types of metal powders from the table have a high explosion pressure and therefore a high destructive force.
Metal dust explosion hazard
Metal dust explosion is a serious hazard because of the following consequences:
- Damage to equipment, propagation of the explosion through piping, equipment, ventilation systems.
A metal dust explosion generates a powerful shock wave and a sudden increase in pressure. This leads to deformation, breakage and complete destruction of equipment. The blast wave can rupture or deform pipelines, which can lead to a leak of hazardous substances and make the situation worse. The most dangerous is the cascading propagation of an explosion through dust removal and ventilation systems. Secondary explosions caused by the uplift of settled particles are almost always more powerful and destructive than the original explosion.
- Risk to life and health of personnel.
The blast wave, combustion products, flying debris and fragments of destroyed equipment, collapse of structures – all these pose a lethal danger to people in the vicinity.
- Financial losses and production stoppage.
Financial costs to rebuild or completely replace equipment.
Losses associated with production stoppage due to investigation and remediation of the incident.
Compensation payments if workers are killed or injured as a result of the explosion.
- Deterioration of image and loss of credibility.
Information about an explosion at a company can cause a serious blow to the company's reputation and lead to a loss of confidence on the part of customers, partners and investors.
Examples of metal dust explosion incidents
Over the past few years, there were many incidents involving metal dust explosions around the world. Below we will provide some of them.
| Photo | Details |
|---|---|
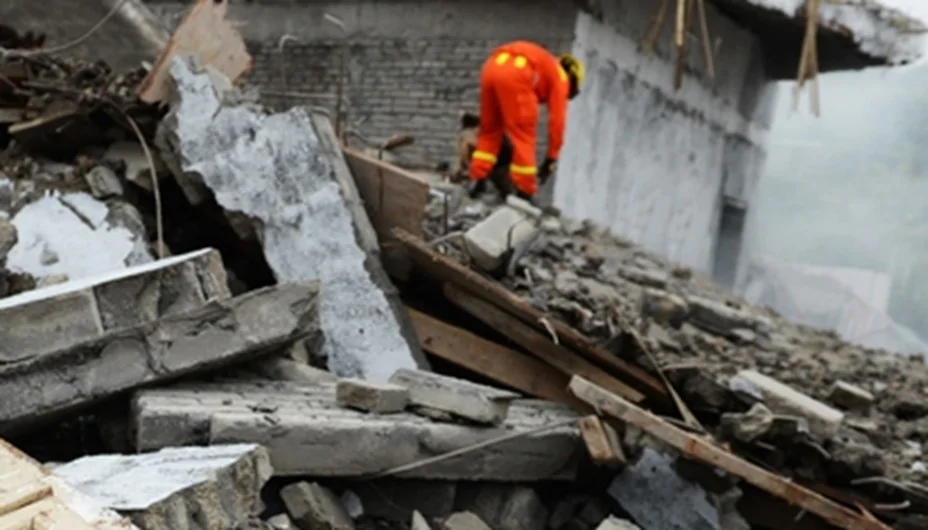 |
Taiwan, 2022. AIDC's aerospace facility The explosion occurred after accumulated aluminum alloy dust ignited. Seven people were taken to hospital where one of them later died. Aerospace Industrial Development Corporation (AIDC) is one of Taiwan's major defense contractors and manufactures and maintains fighter jets and aircraft components. |
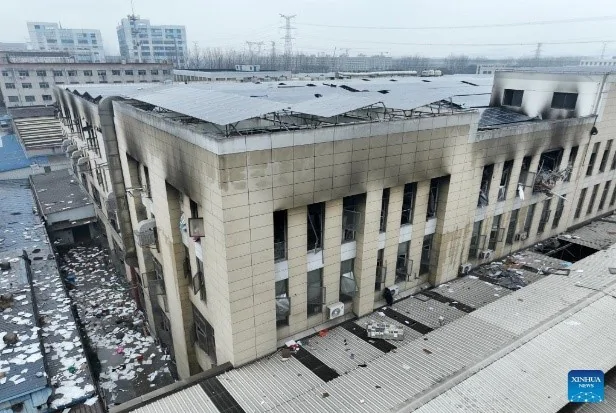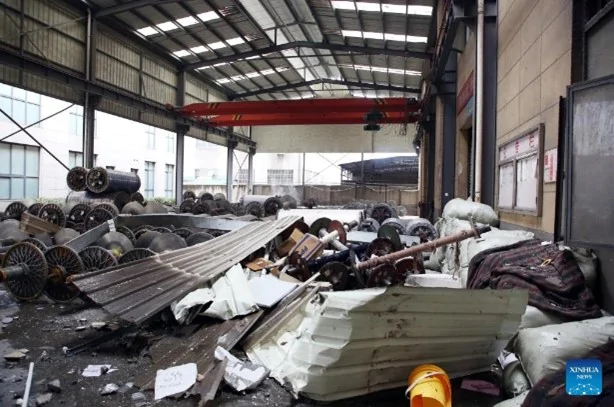  |
China, 2024. Shenrong Metal Technology Limited Tragedy occurred due to the explosion of metal dust in the production hall. As a result, 8 people were killed and 8 others were injured. The company is engaged in the research and development of metal products for construction. |
| The USA, 2025. Powder Alloy Corporation's metal fabrication plant The incident occurred when aluminum dust was pressed into a dust collector, resulting in an explosion and subsequent fire. No one was injured and the fire was extinguished, the extent and cost of the damage is unknown at this time. The company manufactures and supplies metal, ceramic and carbide powders worldwide. |
|
How to protect a plant from metal dust explosions?
The effective protection of a plant from the devastating effects of metal powder explosions requires a comprehensive approach that includes organizational measures, the installation of aspiration systems and the use of explosion protection systems.
Organizational measures
- Training.
Regular briefings on dust explosion hazard, its sources, safe work and actions in case of emergency.
- Dust quantity control.
Wet cleaning, explosion-proof vacuum cleaners, barriers, optimization of processes and monitoring of suspended solids concentrations.
- Regulations.
Developing and following instructions for safe operation and maintenance of equipment, cleaning, disposal and control of flammable metal dust.
Installation of aspiration systems
Aspiration system captures dust at the places of its formation, carries it through ducts to the filter, where the separation of particles from the air takes place, after which the cleaned air is removed, and the collected powder will remain in the hopper. Metalworking machine tables often have special chutes and openings for heavy metal shavings.
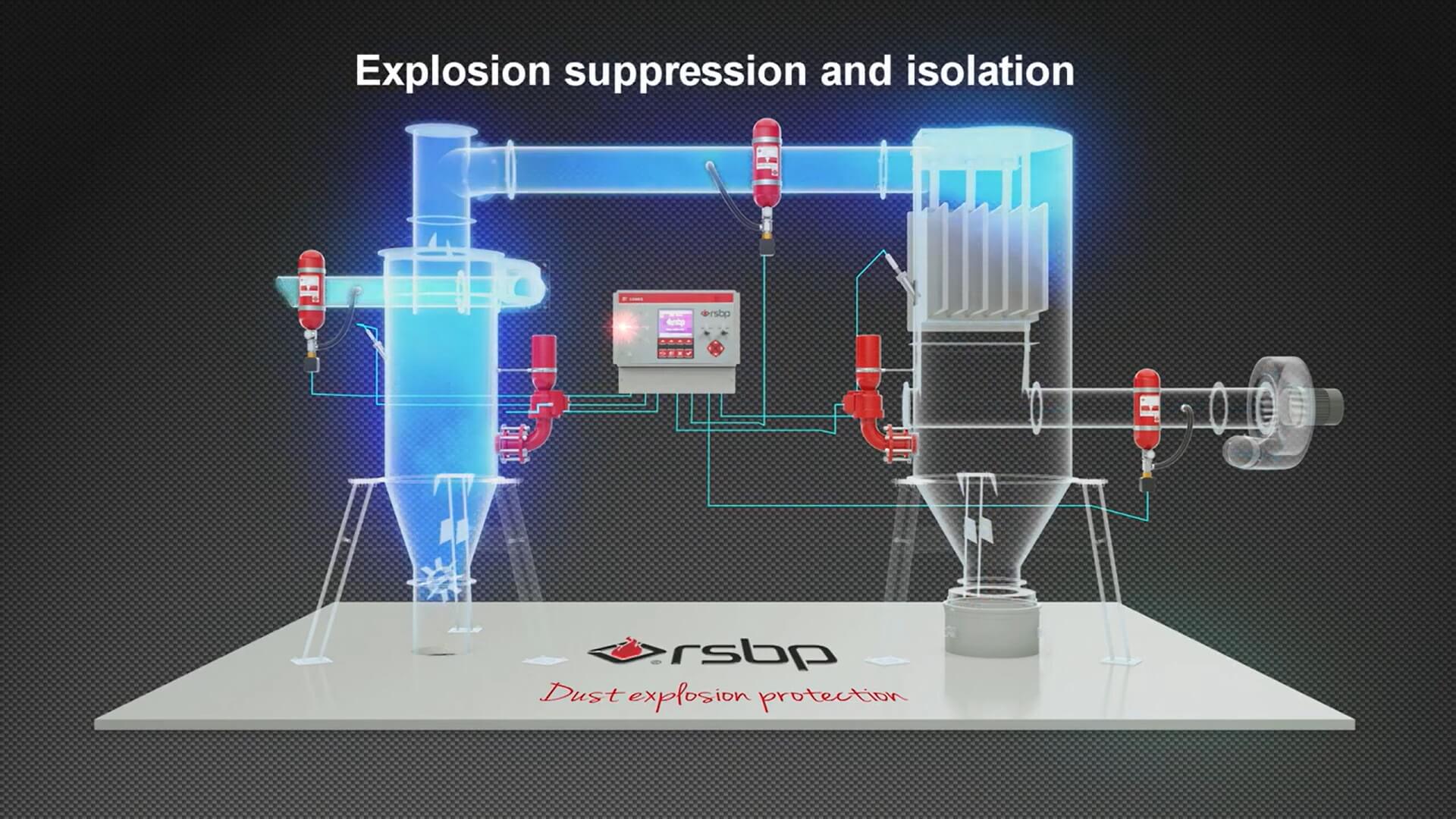
Installation of explosion protection systems
An effective measure to prevent incidents involving dust explosions in production is the implementation of protective systems.
| Explosion venting panels | |
 |
VENT PRO S During the normal course of the process, Vent PRO S closes special process openings in the structure of the equipment to be protected. In the event of an accident, the pressure rises and the bursting disc opens. The products of the explosion – flames, burning particles, blast wave – are released and discharged into the environment. |
| Flameless explosion venting devices | |
 |
FLEX C In the event of an explosion, pressure rises in the equipment and the VMP explosion discharge diaphragm opens. Flames, burning dust, gases will be discharged into the FLEX device. For metals, only the FLEX Type C flame arrestor is suitable, as it has a cylindrical shape allowing for a 360 degree overpressure release around itself, thus providing minimum resistance to release. The maximum Kst of the dust must not exceed 300 bar•m/s. |
| Explosion isolation valves | |
 |
B-FLAP In normal operation the check valve flap is in the open position and is supported by the RPD mechanism. In the event of an explosion due to blast wave action, the flap is closed and locked in the closed position. |
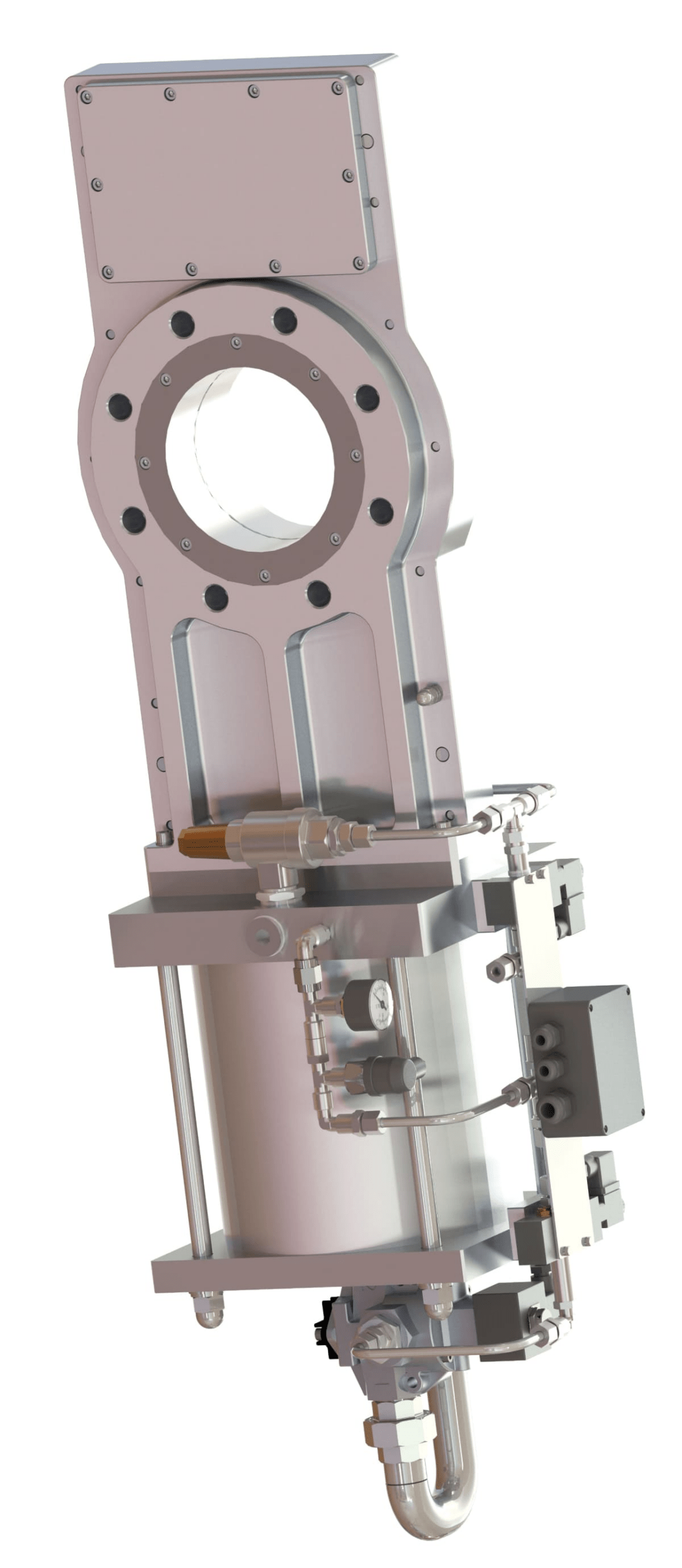 |
GATEX In case of explosion and sudden pressure increase, the sensors immediately transmit a signal to the control center. The controller activates the pneumatic actuator of the gate valve, ensuring its quick closing (response time – milliseconds) and closing the dangerous section of the pipeline. |
| HRD explosion suppression systems | |
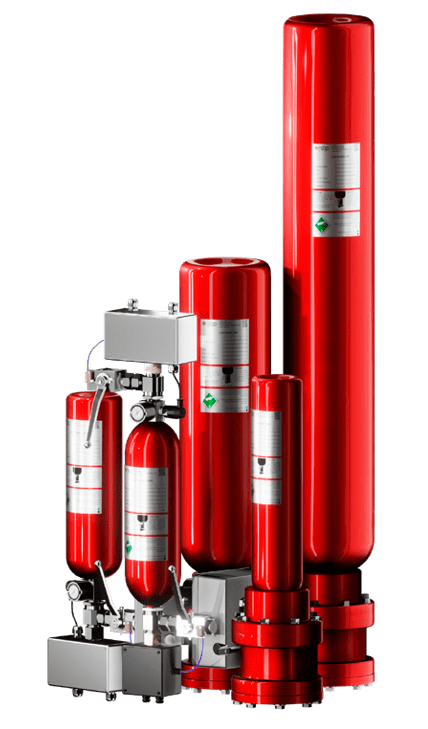 |
HRD HRD system detects an explosion in equipment at an early stage using highly sensitive sensors and effectively suppresses it by applying an explosion suppressant. |
Conclusion
Minimizing the probability of metal powder explosions, including those due to self-ignition of particles, is a priority in plant safety. Laboratory testing of dust samples from a particular plant is required to characterize explosion hazards and then develop steps to ensure the safety of the facility. In addition to mandatory organizational measures and aspiration systems, explosion containment systems play a key role. They minimize damage, protect personnel and preserve the integrity of the plant.
