Dust explosions might sound like something out of a sci-fi movie, but they are very real and can be devastating. So, what is a dust explosion? It's when fine particles in the air ignite and explode. Understanding dust explosions is crucial because they pose significant risks in many industries, leading to property damage, injuries, and even fatalities. This article will dive into the details of dust explosions, covering everything from the science behind them to prevention measures.
What is a Dust Explosion?
A dust explosion occurs when fine particles suspended in the air ignite. The resulting explosion can cause extensive damage due to the rapid expansion of gases and the subsequent pressure wave.
Common Locations for Dust Explosions
Dust explosions can happen in various locations, including factories, grain silos, and even homes. Any place where fine particulate matter is present and can become airborne is at risk.
Types of Combustible Dust
Combustible dust can originate from various materials. Some common types include:
-
Agricultural Dust: Grain, sugar, and flour dust
-
Metal Dust: Aluminum, magnesium, and iron dust
-
Chemical Dust: Pharmaceuticals, pesticides, and certain fertilizers
-
Wood and Paper Dust: Sawdust, paper dust, and pulp dust
-
Textile Dust: Cotton, wool, and synthetic fiber dust
-
Coal and Carbon Dust: Coal, charcoal, and soot
-
Plastic Dust: Polyethylene, polypropylene, and other synthetic polymer dust
Understanding the specific types of combustible dust in an environment is crucial for implementing effective safety measures to prevent dust explosions.
How Dangerous is a Dust Explosion?
Dust explosions present a serious hazard in many industries, often leading to catastrophic outcomes. When fine particles in the air ignite, the explosion can cause immediate and severe damage to buildings and machinery, potentially resulting in injuries or fatalities. Survivors may suffer long-term health issues, including respiratory problems and psychological trauma. The risk is especially high in sectors such as agriculture, manufacturing, food processing, and woodworking, where combustible dusts are common. Recognizing the dangers and implementing strict safety measures is essential to prevent these devastating incidents.
Health and Safety Risks
-
Injury and Fatality: Dust explosions can cause severe injuries and fatalities. The intense blast can result in burns, blunt force trauma from debris, and asphyxiation from smoke and dust inhalation.
-
Respiratory Issues: Even if a dust explosion does not occur, exposure to fine particulate matter can cause chronic respiratory problems, including asthma, bronchitis, and other lung conditions.
-
Toxic Exposure: Some types of dust, particularly chemical or metal dust, can be toxic when inhaled, leading to long-term health problems such as poisoning or cancer.
-
Secondary Explosions: Initial explosions can disturb settled dust, creating a cloud that may ignite and cause secondary explosions, further increasing the risk of injury and death.
Potential Damage to Infrastructure
-
Structural Damage: The force of a dust explosion can severely damage buildings and structures. Walls can collapse, roofs can be blown off, and support beams can be compromised.
-
Equipment Destruction: Industrial equipment can be destroyed or rendered inoperable, leading to significant financial losses and prolonged downtime for businesses.
-
Fire: Explosions often result in fires that can spread quickly, causing further damage to the facility and potentially igniting other combustible materials.
-
Environmental Impact: The release of toxic dust and combustion byproducts into the environment can contaminate air, water, and soil, posing additional health risks and requiring costly cleanup efforts.
-
Economic Losses: Beyond the immediate physical damage, dust explosions can result in substantial economic losses due to halted production, repair costs, insurance claims, and potential legal liabilities.
The dangers associated with dust explosions necessitate rigorous safety measures and continuous monitoring in environments where combustible dust is present. Implementing proper ventilation, dust control systems, regular cleaning, and maintenance, along with employee training on handling and emergency procedures, are critical steps in mitigating the risks.
How Do Dust Explosions Happen?
Dust explosions occur through a specific chain of events that transform a simple accumulation of dust into a highly destructive explosion. Understanding the mechanism behind these explosions and analyzing real-world incidents can help in developing effective prevention strategies.
Conditions Required for an Explosion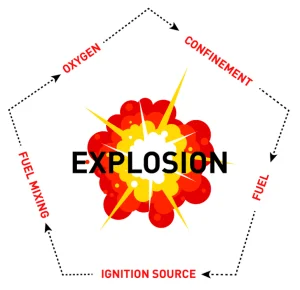
-
Fuel: Fine, combustible dust particles.
-
Oxygen: Present in the air.
-
Confinement: An enclosed space.
-
Dispersion: Dust particles must be suspended in the air.
-
Ignition Source: A spark, flame, or heat.
The Mechanism Behind Dust Explosions
-
Accumulation of Combustible Dust: Fine particles of combustible materials accumulate in an environment. These particles can come from various sources such as manufacturing processes, agricultural activities, or mining operations.
-
Dispersion of Dust in the Air: The dust becomes suspended in the air, forming a dust cloud. This can happen through disturbances like cleaning activities, equipment malfunctions, or even minor vibrations.
-
Confinement of the Dust Cloud: The dust cloud is often in a confined or semi-confined space. This confinement allows pressure to build up during the explosion, amplifying its force.
-
Presence of an Ignition Source: An ignition source, such as an open flame, electrical spark, static electricity, hot surfaces, or friction heat, ignites the dust cloud.
-
Combustion and Explosion: Upon ignition, the dust particles rapidly combust, releasing energy in the form of heat and pressure. This results in an explosion that can cause significant damage and pose serious risks to health and safety.
Case Studies and Incident Analysis
-
Imperial Sugar Refinery Explosion (2008): A catastrophic dust explosion at the Imperial Sugar refinery in Georgia killed 14 workers and injured 36 others. Poor housekeeping practices, inadequate dust control measures, and lack of proper explosion venting systems contributed to the disaster.
-
West Pharmaceutical Services Explosion (2003): A dust explosion in North Carolina killed six people and injured dozens. The explosion was triggered by polyethylene dust that had accumulated in the ceiling space. This incident highlighted the dangers of hidden dust accumulations and the need for regular cleaning and maintenance.
-
Rouse Polymerics International Explosion (2002): A rubber manufacturing plant in Mississippi experienced a dust explosion that resulted in five fatalities. The ignition of rubber dust due to a spark from malfunctioning equipment caused the explosion. This incident underscored the importance of equipment maintenance and effective dust collection systems.
Dust Explosion Prevention and Protection
Preventing and protecting against dust explosions involves a multi-faceted approach that integrates advanced technology, stringent safety protocols, and practical preventative measures. Here’s an overview of key strategies and systems that can be employed to mitigate the risks of dust explosions.
Advanced Explosion Protection Systems
-
Explosion Venting: Designed to relieve pressure by providing a controlled pathway for expanding gases to escape. Vents should be strategically placed in areas prone to dust accumulation.
-
Explosion Suppression Systems: These systems detect and suppress explosions in their early stages using sensors and suppressant agents. Install sensors to detect early signs of an explosion and deploy suppression agents to quench it.
-
Explosion Isolation Systems: Isolation systems prevent the propagation of explosions between interconnected equipment or process areas. Use barriers to isolate different sections of a facility.
-
Dust Collection Systems: High-efficiency dust collection systems capture and contain combustible dust. Regularly maintain and clean dust collectors, ensuring they are equipped with proper filters.
Developing and Implementing Safety Protocols
-
Risk Assessment: Conduct thorough risk assessments to identify potential sources of combustible dust and evaluate the likelihood and potential impact of dust explosions.
-
Housekeeping and Maintenance: Establish regular cleaning schedules to prevent dust accumulation and ensure equipment is regularly maintained.
-
Employee Training and Education: Provide comprehensive training for employees on the hazards of combustible dust, proper handling, and emergency response procedures.
-
Emergency Response Planning: Develop and regularly update emergency response plans that include procedures for evacuation, firefighting, and first aid in the event of a dust explosion.
Practical Steps for Prevention
-
Control Dust Sources: Identify and control processes that generate dust. Implement dust control measures such as wetting agents and enclosed conveying systems.
-
Implement Ventilation: Ensure adequate ventilation in all areas where dust is generated to prevent dust clouds from forming. Use local exhaust ventilation systems to capture dust at the source.
-
Minimize Ignition Sources: Eliminate potential ignition sources by ensuring electrical equipment is dust-rated, controlling static electricity, and maintaining safe hot work practices.
-
Regular Inspections: Conduct regular inspections to identify and rectify potential hazards such as dust build-up and equipment wear and tear.
-
Compliance with Regulations: Adhere to industry regulations and standards to ensure that all safety measures meet required guidelines.
Preventing and protecting against dust explosions requires a comprehensive approach that includes advanced explosion protection systems, the development and implementation of stringent safety protocols, and practical preventative measures. By integrating these strategies, industries can significantly reduce the risk of dust explosions, safeguarding both personnel and infrastructure.
